Reading Hex Data Dump Wireshark Octet Format
Screenshots
wireshark 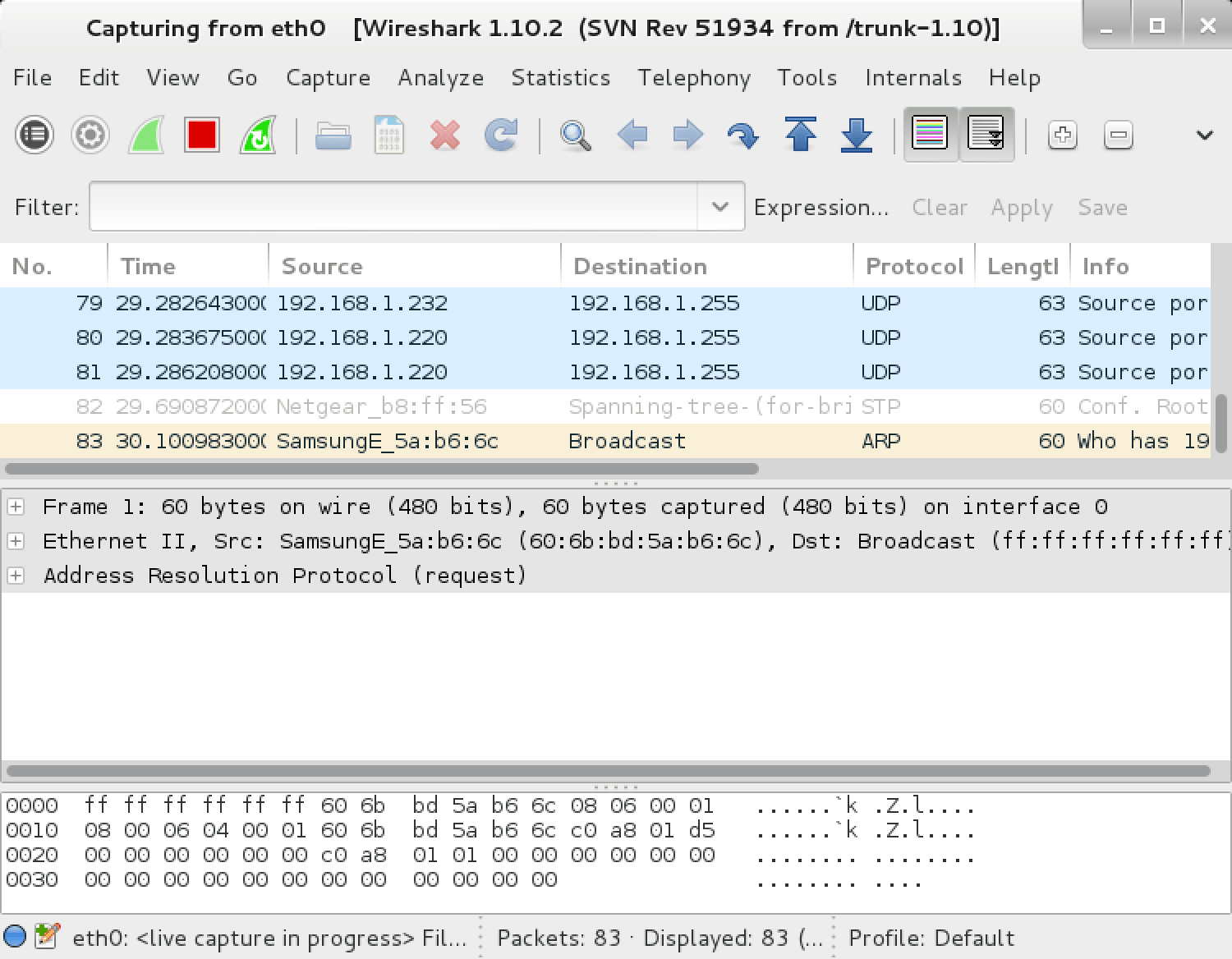
tshark Usage Instance
[email protected]:~# tshark -f "tcp port 80" -i eth0 Packages and Binaries:
libwireshark-information
The libwireshark library provides the network packet dissection services developed past the Wireshark project.
This parcel contains the platform contained files.
Installed size: 7.06 MB
How to install: sudo apt install libwireshark-data
libwireshark-dev
The "libwireshark" library provides the network packet dissection services developed by the Wireshark project.
This packet contains the static library and the C header files that are needed for applications to use libwireshark services.
Installed size: 4.57 MB
How to install: sudo apt install libwireshark-dev
- libwireshark15
- libwiretap-dev
- libwsutil-dev
libwireshark15
The libwireshark library provides the network packet dissection services adult by the Wireshark project.
Installed size: 102.12 MB
How to install: sudo apt install libwireshark15
- libbcg729-0
- libbrotli1
- libc-ares2
- libc6
- libgcrypt20
- libglib2.0-0
- libgnutls30
- libk5crypto3
- libkrb5-3
- liblua5.two-0
- liblz4-1
- libnghttp2-14
- libsbc1
- libsmi2ldbl
- libsnappy1v5
- libspandsp2
- libwireshark-data
- libwiretap12
- libwsutil13
- libxml2
- libzstd1
- zlib1g
libwiretap-dev
Wiretap, part of the Wireshark project, is a library that allows i to read and write several bundle capture file formats.
Supported formats are:
- Libpcap
- Sniffer
- LANalyzer
- Network Monitor
- "snoop"
- "iptrace"
- Sniffer Basic (NetXRay)/Windows Sniffer Pro
- RADCOM WAN/LAN Analyzers
- Lucent/Ascend access products
- HP-UX nettl
- Toshiba ISDN Router
- ISDN4BSD "i4btrace" utility
- Cisco Secure Intrusion Detection Organization iplogging facility
- pppd logs (pppdump-format files)
- VMS TCPTRACE
- DBS Etherwatch (text format)
- Catapult DCT2000 (.out files)
Wiretap's shortcomings are: no filter capability and no support for packet capture.
This packet contains the static library and the C header files.
Installed size: 305 KB
How to install: sudo apt install libwiretap-dev
- libwiretap12
libwiretap12
Wiretap, office of the Wireshark project, is a library that allows one to read and write several packet capture file formats.
Supported formats are:
- Libpcap
- Sniffer
- LANalyzer
- Network Monitor
- "snoop"
- "iptrace"
- Sniffer Basic (NetXRay)/Windows Sniffer Pro
- RADCOM WAN/LAN Analyzers
- Lucent/Ascend admission products
- HP-UX nettl
- Toshiba ISDN Router
- ISDN4BSD "i4btrace" utility
- Cisco Secure Intrusion Detection System iplogging facility
- pppd logs (pppdump-format files)
- VMS TCPTRACE
- DBS Etherwatch (text format)
- Catapult DCT2000 (.out files)
Wiretap's shortcomings are: no filter capability and no support for packet capture.
Installed size: 801 KB
How to install: sudo apt install libwiretap12
- libc6
- libglib2.0-0
- liblz4-one
- libwsutil13
- libzstd1
- zlib1g
libwsutil-dev
The libwsutil library provides utility functions for libwireshark6.
This packet contains the static library and the C header files that are needed for applications to employ the libwsutil library.
Installed size: 417 KB
How to install: sudo apt install libwsutil-dev
- libwsutil13
libwsutil13
The libwsutil library provides utility functions for libwireshark15.
Installed size: 363 KB
How to install: sudo apt install libwsutil13
- libc6
- libgcrypt20
- libglib2.0-0
- libgnutls30
tshark
Wireshark is a network "sniffer" - a tool that captures and analyzes packets off the wire. Wireshark can decode too many protocols to list hither.
This bundle provides the console version of wireshark, named "tshark".
Installed size: 501 KB
How to install: sudo apt install tshark
- libc6
- libglib2.0-0
- libpcap0.8
- libwireshark15
- libwiretap12
- libwsutil13
- wireshark-mutual
- zlib1g
tshark
Dump and analyze network traffic
[email protected]:~# tshark -h TShark (Wireshark) three.6.0 (Git v3.half dozen.0 packaged as 3.6.0-1) Dump and analyze network traffic. See https://www.wireshark.org for more than information. Usage: tshark [options] ... Capture interface: -i <interface>, --interface <interface> proper noun or idx of interface (def: offset non-loopback) -f <capture filter> packet filter in libpcap filter syntax -s <snaplen>, --snapshot-length <snaplen> parcel snapshot length (def: advisable maximum) -p, --no-promiscuous-style don't capture in promiscuous fashion -I, --monitor-mode capture in monitor mode, if available -B <buffer size>, --buffer-size <buffer size> size of kernel buffer (def: 2MB) -y <link type>, --linktype <link type> link layer blazon (def: commencement appropriate) --fourth dimension-postage stamp-type <type> timestamp method for interface -D, --list-interfaces print list of interfaces and exit -L, --list-data-link-types print list of link-layer types of iface and get out --list-fourth dimension-stamp-types impress list of timestamp types for iface and exit Capture stop atmospheric condition: -c <packet count> stop after n packets (def: space) -a <autostop cond.> ..., --autostop <autostop cond.> ... elapsing:NUM - stop later on NUM seconds filesize:NUM - stop this file after NUM KB files:NUM - stop after NUM files packets:NUM - stop after NUM packets Capture output: -b <ringbuffer opt.> ..., --ring-buffer <ringbuffer opt.> duration:NUM - switch to next file after NUM secs filesize:NUM - switch to side by side file after NUM KB files:NUM - ringbuffer: supplant afterward NUM files packets:NUM - switch to next file afterwards NUM packets interval:NUM - switch to next file when the time is an verbal multiple of NUM secs Input file: -r <infile>, --read-file <infile> set the filename to read from (or '-' for stdin) Processing: -two perform a two-pass assay -Chiliad <package count> perform session auto reset -R <read filter>, --read-filter <read filter> packet Read filter in Wireshark display filter syntax (requires -2) -Y <brandish filter>, --display-filter <display filter> packet displaY filter in Wireshark brandish filter syntax -n disable all proper noun resolutions (def: "mNd" enabled, or as set in preferences) -North <proper name resolve flags> enable specific name resolution(s): "mnNtdv" -d <layer_type>==<selector>,<decode_as_protocol> ... "Decode Every bit", see the homo folio for details Example: tcp.port==8888,http -H <hosts file> read a listing of entries from a hosts file, which volition then exist written to a capture file. (Implies -W n) --enable-protocol <proto_name> enable dissection of proto_name --disable-protocol <proto_name> disable dissection of proto_name --enable-heuristic <short_name> enable autopsy of heuristic protocol --disable-heuristic <short_name> disable dissection of heuristic protocol Output: -w <outfile|-> write packets to a pcapng-format file named "outfile" (or '-' for stdout) --capture-comment <comment> add a capture file comment, if supported -C <config profile> start with specified configuration profile -F <output file type> set the output file type, default is pcapng an empty "-F" option will list the file types -V add output of bundle tree (Bundle Details) -O <protocols> Simply show packet details of these protocols, comma separated -P, --impress print packet summary even when writing to a file -S <separator> the line separator to impress between packets -ten add output of hex and ASCII dump (Packet Bytes) -T pdml|ps|psml|json|jsonraw|ek|tabs|text|fields|? format of text output (def: text) -j <protocolfilter> protocols layers filter if -T ek|pdml|json selected (e.one thousand. "ip ip.flags text", filter does not expand child nodes, unless child is specified also in the filter) -J <protocolfilter> top level protocol filter if -T ek|pdml|json selected (e.g. "http tcp", filter which expands all child nodes) -due east <field> field to print if -Tfields selected (e.grand. tcp.port, _ws.col.Info) this choice can be repeated to impress multiple fields -E<fieldsoption>=<value> gear up options for output when -Tfields selected: bom=y|n print a UTF-8 BOM header=y|n switch headers on and off separator=/t|/southward|<char> select tab, space, printable character equally separator occurrence=f|l|a print first, final or all occurrences of each field aggregator=,|/s|<char> select comma, space, printable character as aggregator quote=d|s|northward select double, single, no quotes for values -t a|ad|adoy|d|dd|east|r|u|ud|udoy output format of time stamps (def: r: rel. to first) -u s|hms output format of seconds (def: s: seconds) -l flush standard output after each packet -q be more tranquility on stdout (e.g. when using statistics) -Q only log true errors to stderr (quieter than -q) -1000 enable group read access on the output file(due south) -W northward Salve extra information in the file, if supported. due north = write network address resolution data -X <key>:<value> eXtension options, come across the man page for details -U tap_name PDUs consign mode, see the man page for details -z <statistics> various statistics, encounter the homo page for details --export-objects <protocol>,<destdir> save exported objects for a protocol to a directory named "destdir" --export-tls-session-keys <keyfile> export TLS Session Keys to a file named "keyfile" --color colour output text similarly to the Wireshark GUI, requires a final with 24-bit colour back up As well supplies colour attributes to pdml and psml formats (Note that attributes are nonstandard) --no-duplicate-keys If -T json is specified, merge duplicate keys in an object into a single key with as value a json array containing all values --elastic-mapping-filter <protocols> If -G elastic-mapping is specified, put but the specified protocols within the mapping file Diagnostic output: --log-level <level> sets the active log level ("disquisitional", "warning", etc.) --log-fatal <level> sets level to abort the plan ("critical" or "warning") --log-domains <[!]list> comma separated list of the agile log domains --log-debug <[!]list> comma separated list of domains with "debug" level --log-noisy <[!]list> comma separated list of domains with "noisy" level --log-file <path> file to output messages to (in addition to stderr) Miscellaneous: -h, --help display this help and exit -5, --version display version info and exit -o <name>:<value> ... override preference setting -K <keytab> keytab file to utilize for kerberos decryption -G [written report] dump one of several bachelor reports and get out default study="fields" use "-G help" for more help Dumpcap can benefit from an enabled BPF JIT compiler if bachelor. You might want to enable information technology by executing: "repeat 1 > /proc/sys/internet/core/bpf_jit_enable" Note that this can make your arrangement less secure! wireshark
Wireshark is a network "sniffer" - a tool that captures and analyzes packets off the wire. Wireshark tin can decode too many protocols to list here.
This is a meta-package for Wireshark.
Installed size: 148 KB
How to install: sudo apt install wireshark
- wireshark-qt
wireshark-common
Wireshark is a network "sniffer" - a tool that captures and analyzes packets off the wire. Wireshark can decode too many protocols to list here.
This package provides files common to both wireshark and tshark (the console version).
Installed size: ane.39 MB
How to install: sudo apt install wireshark-mutual
- debconf
- debconf | debconf-2.0
- libc6
- libcap2
- libcap2-bin
- libgcrypt20
- libglib2.0-0
- libmaxminddb0
- libnl-3-200
- libnl-genl-3-200
- libpcap0.8
- libspeexdsp1
- libssh-gcrypt-4
- libsystemd0
- libwireshark15
- libwiretap12
- libwsutil13
- zlib1g
capinfos
Prints information nearly capture files
[email protected]:~# capinfos -h Capinfos (Wireshark) 3.six.0 (Git v3.6.0 packaged as 3.six.0-1) Print various information (infos) almost capture files. See https://world wide web.wireshark.org for more than information. Usage: capinfos [options] <infile> ... General infos: -t display the capture file type -Eastward brandish the capture file encapsulation -I display the capture file interface information -F display additional capture file information -H brandish the SHA256, RIPEMD160, and SHA1 hashes of the file -yard brandish the capture comment Size infos: -c display the number of packets -south display the size of the file (in bytes) -d display the total length of all packets (in bytes) -l display the packet size limit (snapshot length) Time infos: -u display the capture duration (in seconds) -a display the capture start fourth dimension -eastward brandish the capture terminate time -o brandish the capture file chronological status (True/False) -South brandish start and cease times every bit seconds Statistic infos: -y display average data rate (in bytes/sec) -i display average information charge per unit (in bits/sec) -z display average packet size (in bytes) -x display average package rate (in packets/sec) Metadata infos: -north display number of resolved IPv4 and IPv6 addresses -D brandish number of decryption secrets Output format: -L generate long report (default) -T generate tabular array study -M display machine-readable values in long reports Table report options: -R generate header record (default) -r practise not generate header tape -B separate infos with TAB grapheme (default) -k carve up infos with comma (,) character -b separate infos with Space character -N practice not quote infos (default) -q quote infos with single quotes (') -Q quote infos with double quotes (") Miscellaneous: -h, --help display this assistance and exit -five, --version display version info and exit -C abolish processing if file open fails (default is to continue) -A generate all infos (default) -K disable displaying the capture annotate Options are processed from left to correct club with later options superseding or adding to earlier options. If no options are given the default is to display all infos in long report output format. captype
Prints the types of capture files
[electronic mail protected]:~# captype -h Captype (Wireshark) three.half-dozen.0 (Git v3.6.0 packaged as 3.half dozen.0-1) Print the file types of capture files. See https://world wide web.wireshark.org for more than information. Usage: captype [options] <infile> ... Miscellaneous: -h, --assistance display this help and exit -v, --version brandish version info and exit dumpcap
Dump network traffic
[email protected]:~# dumpcap -h Dumpcap (Wireshark) 3.6.0 (Git v3.6.0 packaged every bit 3.half-dozen.0-one) Capture network packets and dump them into a pcapng or pcap file. Encounter https://www.wireshark.org for more information. Usage: dumpcap [options] ... Capture interface: -i <interface>, --interface <interface> proper noun or idx of interface (def: first non-loopback), or for remote capturing, utilize 1 of these formats: rpcap://<host>/<interface> [email protected]<host>:<port> --ifname <name> name to use in the capture file for a pipe from which we're capturing --ifdescr <clarification> description to apply in the capture file for a pipe from which we're capturing -f <capture filter> packet filter in libpcap filter syntax -s <snaplen>, --snapshot-length <snaplen> bundle snapshot length (def: advisable maximum) -p, --no-promiscuous-mode don't capture in promiscuous manner -I, --monitor-fashion capture in monitor mode, if available -B <buffer size>, --buffer-size <buffer size> size of kernel buffer in MiB (def: 2MiB) -y <link type>, --linktype <link type> link layer type (def: get-go appropriate) --fourth dimension-postage stamp-type <type> timestamp method for interface -D, --list-interfaces print list of interfaces and exit -L, --list-data-link-types print list of link-layer types of iface and exit --list-time-stamp-types print list of timestamp types for iface and exit -d print generated BPF code for capture filter -k <freq>,[<type>],[<center_freq1>],[<center_freq2>] gear up aqueduct on wifi interface -S impress statistics for each interface once per second -M for -D, -L, and -S, produce machine-readable output End conditions: -c <packet count> stop after n packets (def: infinite) -a <autostop cond.> ..., --autostop <autostop cond.> ... duration:NUM - stop after NUM seconds filesize:NUM - stop this file after NUM kB files:NUM - end afterward NUM files packets:NUM - stop later NUM packets Output (files): -w <filename> name of file to salvage (def: tempfile) -thousand enable grouping read access on the output file(s) -b <ringbuffer opt.> ..., --band-buffer <ringbuffer opt.> duration:NUM - switch to next file after NUM secs filesize:NUM - switch to next file after NUM kB files:NUM - ringbuffer: supplant after NUM files packets:NUM - ringbuffer: supersede afterward NUM packets interval:NUM - switch to next file when the time is an exact multiple of NUM secs printname:FILE - impress filename to FILE when written (can use 'stdout' or 'stderr') -north use pcapng format instead of pcap (default) -P utilise libpcap format instead of pcapng --capture-comment <annotate> add a capture comment to the output file (simply for pcapng) Diagnostic output: --log-level <level> sets the active log level ("critical", "alarm", etc.) --log-fatal <level> sets level to arrest the programme ("disquisitional" or "alarm") --log-domains <[!]list> comma separated list of the active log domains --log-debug <[!]list> comma separated listing of domains with "debug" level --log-noisy <[!]list> comma separated list of domains with "noisy" level --log-file <path> file to output letters to (in improver to stderr) Miscellaneous: -N <packet_limit> maximum number of packets buffered within dumpcap -C <byte_limit> maximum number of bytes used for buffering packets within dumpcap -t utilize a separate thread per interface -q don't report packet capture counts -v, --version print version information and leave -h, --help display this help and get out Dumpcap tin can benefit from an enabled BPF JIT compiler if bachelor. Y'all might desire to enable information technology past executing: "repeat 1 > /proc/sys/internet/core/bpf_jit_enable" Note that this can make your system less secure! Example: dumpcap -i eth0 -a duration:60 -w output.pcapng "Capture packets from interface eth0 until 60s passed into output.pcapng" Apply Ctrl-C to cease capturing at any fourth dimension. editcap
Edit and/or translate the format of capture files
[email protected]:~# editcap -h Editcap (Wireshark) 3.6.0 (Git v3.6.0 packaged as 3.6.0-i) Edit and/or translate the format of capture files. See https://www.wireshark.org for more information. Usage: editcap [options] ... <infile> <outfile> [ <bundle#>[-<packet#>] ... ] <infile> and <outfile> must both be nowadays. A single packet or a range of packets can be selected. Packet option: -r go along the selected packets; default is to delete them. -A <kickoff time> only read packets whose timestamp is after (or equal to) the given time. -B <finish time> only read packets whose timestamp is before the given time. Time format for -A/-B options is YYYY-MM-DDThh:mm:ss[.nnnnnnnnn][Z|+-hh:mm] Unix epoch timestamps are as well supported. Duplicate packet removal: --novlan remove vlan info from packets before checking for duplicates. -d remove packet if indistinguishable (window == five). -D <dup window> remove packet if indistinguishable; configurable <dup window>. Valid <dup window> values are 0 to 1000000. NOTE: A <dup window> of 0 with -v (verbose option) is useful to print MD5 hashes. -w <dup time window> remove packet if duplicate bundle is found EQUAL TO OR LESS THAN <dup time window> prior to current packet. A <dup time window> is specified in relative seconds (due east.yard. 0.000001). NOTE: The use of the 'Duplicate packet removal' options with other editcap options except -v may not always piece of work as expected. Specifically the -r, -t or -S options volition very likely Non have the desired event if combined with the -d, -D or -w. --skip-radiotap-header skip radiotap header when checking for packet duplicates. Useful when processing packets captured by multiple radios on the same aqueduct in the vicinity of each other. Packet manipulation: -southward <snaplen> truncate each packet to max. <snaplen> bytes of data. -C [offset:]<choplen> chop each bundle by <choplen> bytes. Positive values chop at the packet beginning, negative values at the package end. If an optional offset precedes the length, then the bytes chopped will be start from that value. Positive offsets are from the packet beginning, negative offsets are from the packet end. Yous can employ this option more than once, allowing up to two chopping regions within a parcel provided that at to the lowest degree ane choplen is positive and at to the lowest degree ane is negative. -L adjust the frame (i.eastward. reported) length when chopping and/or snapping. -t <time aligning> arrange the timestamp of each packet. <time adjustment> is in relative seconds (e.g. -0.five). -Southward <strict adjustment> adjust timestamp of packets if necessary to ensure strict chronological increasing order. The <strict adjustment> is specified in relative seconds with values of 0 or 0.000001 being the nearly reasonable. A negative adjustment value volition modify timestamps so that each packet'south delta time is the absolute value of the adjustment specified. A value of -0 will set all packets to the timestamp of the start packet. -E <error probability> set the probability (between 0.0 and ane.0 incl.) that a item packet byte will exist randomly changed. -o <change showtime> When used in conjunction with -East, skip some bytes from the starting time of the bundle. This allows 1 to preserve some bytes, in guild to have some headers untouched. --seed <seed> When used in conjunction with -E, fix the seed to utilise for the pseudo-random number generator. This allows i to repeat a particular sequence of errors. -I <bytes to ignore> ignore the specified number of bytes at the first of the frame during MD5 hash adding, unless the frame is also short, then the total frame is used. Useful to remove duplicated packets taken on several routers (different mac addresses for case). due east.g. -I 26 in case of Ether/IP will ignore ether(xiv) and IP header(20 - iv(src ip) - 4(dst ip)). -a <framenum>:<comment> Add together or supplant annotate for given frame number Output File(s): -c <packets per file> carve up the bundle output to dissimilar files based on uniform packet counts with a maximum of <packets per file> each. -i <seconds per file> split the packet output to different files based on uniform fourth dimension intervals with a maximum of <seconds per file> each. -F <capture type> ready the output file type; default is pcapng. An empty "-F" pick will list the file types. -T <encap blazon> fix the output file encapsulation type; default is the same as the input file. An empty "-T" selection will list the encapsulation types. --inject-secrets <type>,<file> Insert decryption secrets from <file>. Listing supported underground types with "--inject-secrets help". --discard-all-secrets Discard all decryption secrets from the input file when writing the output file. Does not discard secrets added by "--inject-secrets" in the same command line. --capture-comment <comment> Add a capture file comment, if supported. --discard-capture-comment Discard capture file comments from the input file when writing the output file. Does not discard comments added by "--capture-comment" in the same command line. Miscellaneous: -h display this help and exit. -five verbose output. If -v is used with whatever of the 'Duplicate Parcel Removal' options (-d, -D or -due west) then Packet lengths and MD5 hashes are printed to standard-error. -V, --version print version information and exit. mergecap
Merges two or more capture files into one
[electronic mail protected]:~# mergecap -h Mergecap (Wireshark) 3.6.0 (Git v3.6.0 packaged as 3.half dozen.0-i) Merge two or more capture files into i. See https://www.wireshark.org for more information. Usage: mergecap [options] -w <outfile>|- <infile> [<infile> ...] Output: -a concatenate rather than merge files. default is to merge based on frame timestamps. -s <snaplen> truncate packets to <snaplen> bytes of data. -w <outfile>|- set the output filename to <outfile> or '-' for stdout. -F <capture type> prepare the output file type; default is pcapng. an empty "-F" pick will list the file types. -I <IDB merge way> set the merge style for Interface Description Blocks; default is 'all'. an empty "-I" option will list the merge modes. Miscellaneous: -h display this help and get out. -5 verbose output. -V print version information and get out. mmdbresolve
Read IPv4 and IPv6 addresses and impress their IP geolocation information.
[electronic mail protected]:~# mmdbresolve -h Usage: mmdbresolve -f db_file [-f db_file ...] randpkt
Random packet generator
[email protected]:~# randpkt -h Usage: randpkt [-b maxbytes] [-c count] [-t type] [-r] filename Default max bytes (per parcel) is 5000 Default count is one thousand. -r: random packet type choice Types: arp Accost Resolution Protocol bgp Border Gateway Protocol bvlc BACnet Virtual Link Control dns Domain Proper noun Service eth Ethernet fddi Fiber Distributed Data Interface giop General Inter-ORB Protocol icmp Cyberspace Control Message Protocol ieee802.15.4 IEEE 802.15.4 ip Internet Protocol ipv6 Cyberspace Protocol Version 6 llc Logical Link Command m2m WiMAX M2M Encapsulation Protocol megaco MEGACO nbns NetBIOS-over-TCP Name Service ncp2222 NetWare Core Protocol sctp Stream Control Transmission Protocol syslog Syslog message tds TDS NetLib tcp Transmission Control Protocol tr Token-Band udp User Datagram Protocol usb-linux Universal Serial Bus with Linux specific header If type is not specified, a random packet will be called rawshark
Dump and analyze raw pcap information
[electronic mail protected]:~# rawshark -h Rawshark (Wireshark) 3.6.0 (Git v3.6.0 packaged as 3.half dozen.0-one) Dump and clarify network traffic. Run across https://world wide web.wireshark.org for more information. Usage: rawshark [options] ... Input file: -r <infile> set the piping or file name to read from Processing: -d <encap:linktype>|<proto:protoname> package encapsulation or protocol -F <field> field to display -m virtual memory limit, in bytes -northward disable all name resolution (def: all enabled) -Due north <proper noun resolve flags> enable specific proper name resolution(due south): "mnNtdv" -p use the organisation's packet header format (which may have 64-flake timestamps) -R <read filter> packet filter in Wireshark display filter syntax -s skip PCAP header on input Output: -l affluent output later each packet -S format cord for fields (%D - name, %S - stringval, %N numval) -t advertizement|a|r|d|dd|due east output format of time stamps (def: r: rel. to start) Diagnostic output: --log-level <level> sets the active log level ("critical", "warning", etc.) --log-fatal <level> sets level to abort the program ("disquisitional" or "warning") --log-domains <[!]list> comma separated list of the active log domains --log-debug <[!]list> comma separated list of domains with "debug" level --log-noisy <[!]list> comma separated listing of domains with "noisy" level --log-file <path> file to output messages to (in addition to stderr) Miscellaneous: -h display this help and exit -o <name>:<value> ... override preference setting -five display version info and go out reordercap
Reorder input file by timestamp into output file
[email protected]:~# reordercap -h Reordercap (Wireshark) 3.six.0 (Git v3.6.0 packaged as three.6.0-i) Reorder timestamps of input file frames into output file. Encounter https://world wide web.wireshark.org for more data. Usage: reordercap [options] <infile> <outfile> Options: -n don't write to output file if the input file is ordered. -h display this aid and exit. -v print version information and exit. sharkd
[email protected]:~# sharkd -h Running every bit user "root" and grouping "root". This could be dangerous. Usage: sharkd [<classic_options>|<gold_options>] Classic (classic_options): [-|<socket>] <socket> examples: - unix:/tmp/sharkd.sock - heed on unix file /tmp/sharkd.sock Aureate (gold_options): -a <socket>, --api <socket> heed on this socket -h, --help show this help information -v, --version show version information -C <config profile>, --config-profile <config profile> get-go with specified configuration profile Examples: sharkd -C myprofile sharkd -a tcp:127.0.0.1:4446 -C myprofile Run across the sharkd page of the Wireshark wiki for total details. text2pcap
Generate a capture file from an ASCII hexdump of packets
[electronic mail protected]:~# text2pcap -h Text2pcap (Wireshark) 3.half dozen.0 (Git v3.6.0 packaged as iii.6.0-1) Generate a capture file from an ASCII hexdump of packets. Run across https://world wide web.wireshark.org for more data. Usage: text2pcap [options] <infile> <outfile> where <infile> specifies input filename (utilize - for standard input) <outfile> specifies output filename (use - for standard output) Input: -o hex|oct|dec parse offsets as (h)ex, (o)ctal or (d)ecimal; default is hex. -t <timefmt> treat the text before the packet every bit a engagement/time lawmaking; the specified argument is a format string of the sort supported by strptime. Case: The fourth dimension "ten:15:xiv.5476" has the format code "%H:%Thousand:%S." NOTE: The subsecond component delimiter, '.', must exist given, but no pattern is required; the remaining number is causeless to be fractions of a 2nd. NOTE: Appointment/time fields from the current date/time are used equally the default for unspecified fields. -D the text earlier the packet starts with an I or an O, indicating that the packet is entering or outbound. This is used when generating dummy headers. The indication is but stored if the output format is pcapng. -a enable ASCII text dump identification. The start of the ASCII text dump tin can be identified and excluded from the packet data, even if it looks similar a HEX dump. Note: Do not enable it if the input file does not contain the ASCII text dump. Output: -l <typenum> link-layer type number; default is ane (Ethernet). See https://www.tcpdump.org/linktypes.html for a listing of numbers. Use this option if your dump is a complete hex dump of an encapsulated packet and yous wish to specify the verbal blazon of encapsulation. Example: -l 7 for ARCNet packets. -m <max-packet> max packet length in output; default is 262144 -n use pcapng instead of pcap as output format. -N <intf-name> assign name to the interface in the pcapng file. Prepend dummy header: -eastward <l3pid> prepend dummy Ethernet II header with specified L3PID (in HEX). Example: -e 0x806 to specify an ARP package. -i <proto> prepend dummy IP header with specified IP protocol (in DECIMAL). Automatically prepends Ethernet header as well. Example: -i 46 -4 <srcip>,<destip> prepend dummy IPv4 header with specified dest and source address. Example: -4 x.0.0.one,x.0.0.2 -half dozen <srcip>,<destip> prepend dummy IPv6 header with specified dest and source accost. Example: -6 fe80::202:b3ff:fe1e:8329,2001:0db8:85a3::8a2e:0370:7334 -u <srcp>,<destp> prepend dummy UDP header with specified source and destination ports (in DECIMAL). Automatically prepends Ethernet & IP headers every bit well. Example: -u 1000,69 to make the packets look like TFTP/UDP packets. -T <srcp>,<destp> prepend dummy TCP header with specified source and destination ports (in DECIMAL). Automatically prepends Ethernet & IP headers likewise. Instance: -T l,60 -southward <srcp>,<dstp>,<tag> prepend dummy SCTP header with specified source/dest ports and verification tag (in DECIMAL). Automatically prepends Ethernet & IP headers likewise. Example: -s 30,xl,34 -S <srcp>,<dstp>,<ppi> prepend dummy SCTP header with specified source/dest ports and verification tag 0. Automatically prepends a dummy SCTP Information chunk header with payload protocol identifier ppi. Example: -S 30,twoscore,34 Miscellaneous: -h display this help and exit. -five impress version data and exit. -d evidence detailed debug of parser states. -q generate no output at all (automatically disables -d). wireshark-dev
Wireshark is a network "sniffer" - a tool that captures and analyzes packets off the wire. Wireshark tin decode as well many protocols to list here.
This package provides idl2wrs and other files necessary for developing new packet dissectors.
Installed size: 658 KB
How to install: sudo apt install wireshark-dev
- libglib2.0-dev
- libpcap0.8-dev
- libwireshark-dev
- libwiretap-dev
- omniidl
- python3
- python3-ply
- snacc
asn2deb
Create a Debian bundle for BER monitoring from ASN.1
[email protected]:~# asn2deb -h Usage: /usr/bin/asn2deb <parameters> Parameters are --asn -a asn1file, ASN.i file to use (mandatory) --dbopts -d opts, options for dpkg-buildpackage --email -e address, use electronic mail address --help -h, print help and exit --name -due north name, use user name --preserve -p, do not overwrite files --version -five, print version and exit Example: /usr/bin/asn2deb -e [email protected] -a bar.asn1 -n "My Name" -d "-rfakeroot -uc -united states" idl2deb
Create a Debian package for CORBA monitoring from IDL
[email protected]:~# idl2deb -h Usage: idl2deb [options] Example: idl2deb -e [email protected] -i bar.idl -n "My Proper name" -d "-rfakeroot -uc -us" Options: --version evidence program'due south version number and exit -h, --help show this help message and exit -d opts, --dbopts=opts options for dpkg-buildpackage -e address, --e-mail=address use e-mail address -i idlfile, --idl=idlfile IDL file to use (mandatory) -n name, --name=name use user name -p, --preserve do not overwrite files idl2wrs
CORBA IDL to Wireshark Plugin Generator
[email protected]:~# idl2wrs -h Usage: omniidl -b<back_end> [flags] file1 file2 ... The supported flags are: -Dname[=value] Define name for preprocessor -Uname Undefine name for preprocessor -Idir Include dir in search path for preprocessor -E Run preprocessor only, print on stdout -Ycmd Set control for the preprocessor -North Do not run preprocessor -P Add together defines relevant to platform dependencies (internal utilise) -T Apply a temporary file, not a pipe, for preprocessor output -Wparg[,arg...] Send args to the preprocessor -bback_end Select a back-end to exist used. More than than one permitted -Wbarg[,arg...] Send args to the back-end -nf Exercise not warn most unresolved forwards declarations -nc Do not care for identifiers differing just in example as an error -one thousand Comments after declarations are kept for the back-ends -K Comments before declarations are kept for the back-ends -Cdir Alter directory to dir before writing output -d Dump the parsed IDL and then get out -i Enter interactive mode later on parsing the IDL -pdir Path to omniidl back-ends ($TOP/lib/python) -5 Impress version info so go out -u Print this usage message and exit -v Trace compilation stages wireshark-doctor
Wireshark is a network "sniffer" - a tool that captures and analyzes packets off the wire. Wireshark can decode too many protocols to listing here.
This packet contains Wireshark User's guide, Wireshark Developer's Guide and the Lua Reference.
Installed size: 13.03 MB
How to install: sudo apt install wireshark-doctor
wireshark-gtk
This is a transitional dummy parcel. It can safely be removed.
Installed size: 146 KB
How to install: sudo apt install wireshark-gtk
- wireshark-qt
wireshark-qt
Wireshark is a network "sniffer" - a tool that captures and analyzes packets off the wire. Wireshark can decode likewise many protocols to list here.
This package provides the Qt version of Wireshark.
Installed size: 8.96 MB
How to install: sudo apt install wireshark-qt
- libc6
- libgcc-s1
- libgcrypt20
- libglib2.0-0
- libminizip1
- libnl-3-200
- libnl-genl-3-200
- libnl-route-three-200
- libpcap0.viii
- libqt5core5a
- libqt5gui5 | libqt5gui5-gles
- libqt5multimedia5
- libqt5printsupport5
- libqt5svg5
- libqt5widgets5
- libspeexdsp1
- libstdc++6
- libwireshark15
- libwiretap12
- libwsutil13
- wireshark-mutual
- zlib1g
wireshark
Interactively dump and clarify network traffic
[email protected]:~# wireshark -h Wireshark iii.half-dozen.0 (Git v3.vi.0 packaged as 3.6.0-1) Interactively dump and clarify network traffic. Run into https://world wide web.wireshark.org for more information. Usage: wireshark [options] ... [ <infile> ] Capture interface: -i <interface>, --interface <interface> name or idx of interface (def: commencement non-loopback) -f <capture filter> packet filter in libpcap filter syntax -s <snaplen>, --snapshot-length <snaplen> parcel snapshot length (def: appropriate maximum) -p, --no-promiscuous-way don't capture in promiscuous fashion -1000 start capturing immediately (def: do nothing) -S update package display when new packets are captured -l turn on automatic scrolling while -S is in use -I, --monitor-mode capture in monitor manner, if bachelor -B <buffer size>, --buffer-size <buffer size> size of kernel buffer (def: 2MB) -y <link blazon>, --linktype <link type> link layer type (def: first appropriate) --time-stamp-type <blazon> timestamp method for interface -D, --list-interfaces impress list of interfaces and exit -Fifty, --list-data-link-types print list of link-layer types of iface and exit --list-time-stamp-types print list of timestamp types for iface and exit Capture finish conditions: -c <packet count> stop after north packets (def: infinite) -a <autostop cond.> ..., --autostop <autostop cond.> ... elapsing:NUM - cease afterwards NUM seconds filesize:NUM - cease this file after NUM KB files:NUM - stop later NUM files packets:NUM - cease after NUM packets Capture output: -b <ringbuffer opt.> ..., --band-buffer <ringbuffer opt.> elapsing:NUM - switch to next file after NUM secs filesize:NUM - switch to next file after NUM KB files:NUM - ringbuffer: replace after NUM files packets:NUM - switch to next file after NUM packets interval:NUM - switch to next file when the fourth dimension is an verbal multiple of NUM secs Input file: -r <infile>, --read-file <infile> set the filename to read from (no pipes or stdin!) Processing: -R <read filter>, --read-filter <read filter> bundle filter in Wireshark display filter syntax -northward disable all name resolutions (def: all enabled) -Northward <proper noun resolve flags> enable specific name resolution(south): "mnNtdv" -d <layer_type>==<selector>,<decode_as_protocol> ... "Decode As", come across the man page for details Example: tcp.port==8888,http --enable-protocol <proto_name> enable dissection of proto_name --disable-protocol <proto_name> disable dissection of proto_name --enable-heuristic <short_name> enable autopsy of heuristic protocol --disable-heuristic <short_name> disable dissection of heuristic protocol User interface: -C <config profile> first with specified configuration profile -H hide the capture info dialog during packet capture -Y <brandish filter>, --display-filter <display filter> offset with the given display filter -yard <packet number> go to specified packet number later on "-r" -J <jump filter> jump to the first packet matching the (display) filter -j search backwards for a matching packet afterward "-J" -t a|advertisement|adoy|d|dd|due east|r|u|ud|udoy format of time stamps (def: r: rel. to offset) -u s|hms output format of seconds (def: s: seconds) -X <key>:<value> eXtension options, see human folio for details -z <statistics> show various statistics, run into homo folio for details Output: -w <outfile|-> set the output filename (or '-' for stdout) --capture-comment <comment> add a capture file comment, if supported Diagnostic output: --log-level <level> sets the active log level ("disquisitional", "warning", etc.) --log-fatal <level> sets level to arrest the program ("critical" or "warning") --log-domains <[!]list> comma separated list of the agile log domains --log-debug <[!]list> comma separated list of domains with "debug" level --log-noisy <[!]list> comma separated list of domains with "noisy" level --log-file <path> file to output messages to (in addition to stderr) Miscellaneous: -h, --help display this assist and exit -5, --version display version info and go out -P <key>:<path> persconf:path - personal configuration files persdata:path - personal information files -o <proper noun>:<value> ... override preference or recent setting -1000 <keytab> keytab file to use for kerberos decryption --display <X display> X display to utilise --fullscreen start Wireshark in full screen Updated on: 2022-Feb-x
Source: https://www.kali.org/tools/wireshark/
0 Response to "Reading Hex Data Dump Wireshark Octet Format"
Post a Comment